Leveraging command-line tools will help you gain more control and flexibility over your servers, making it easier to integrate Kamatera services into larger automation frameworks. This is mainly used by DevOps, system administrators, and anyone who wants to use cloud resources programmatically. By using command-line tools, you can:
- Automate server management tasks such as configuration and scaling.
- Easily integrate with other applications.
- Improved efficiency because you can quickly execute commands to check the status of servers.
- Manage servers remotely.
In this article, we will go through all the steps to use SSH for Linux server management and Windows.
1. SSH for Linux
SSH (Secure Shell) provides a secure way to remotely access and manage Linux servers.
First, install an SSH Client:
On Linux/macOS: SSH is pre-installed, so you can directly use the terminal.
- On Windows: Use tools like PuTTY, or OpenSSH (which is built into modern versions).
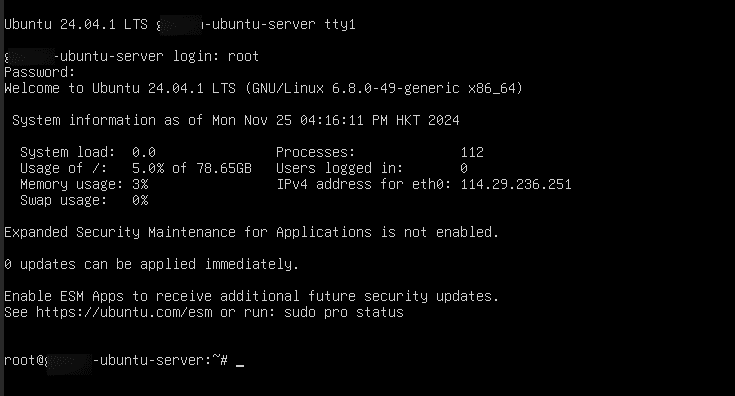
On Linux:
- Login with username and password in your Ubuntu terminal and run the commands below.
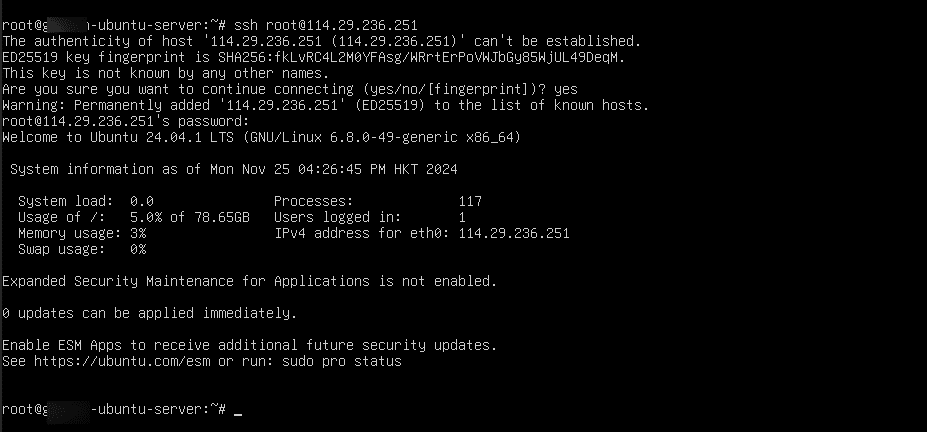
2. Otherwise, connect to the server:
Using Password
Open the terminal and type the below command
Command:
ssh root@<server_ip>
Note: Replace server_ip with your actual Server IP Address.
When asked, type the password that you got from Kamatera and press Enter.
Using SSH Key
If Kamatera gave you a special key file, then type the below command
Command:
ssh -i /path/to/key-file root@<server_ip>
Note: Replace server_ip with your actual Server IP Address.
-
- After connecting, you can use these simple commands in Ubuntu terminal.
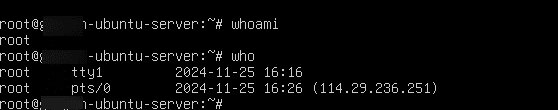
- Check Server status
- To know the name of the currently logged-in user
Command:
whoami
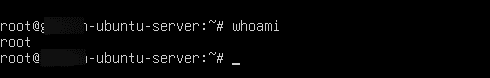
- To see who has logged in
Command:
who
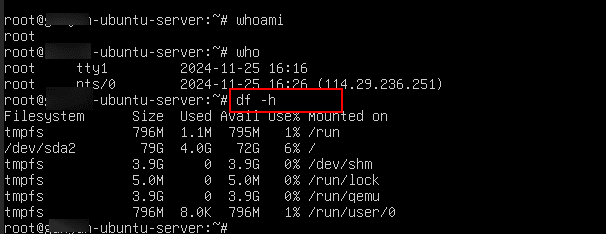
- To check Disk space
Command:
df –h
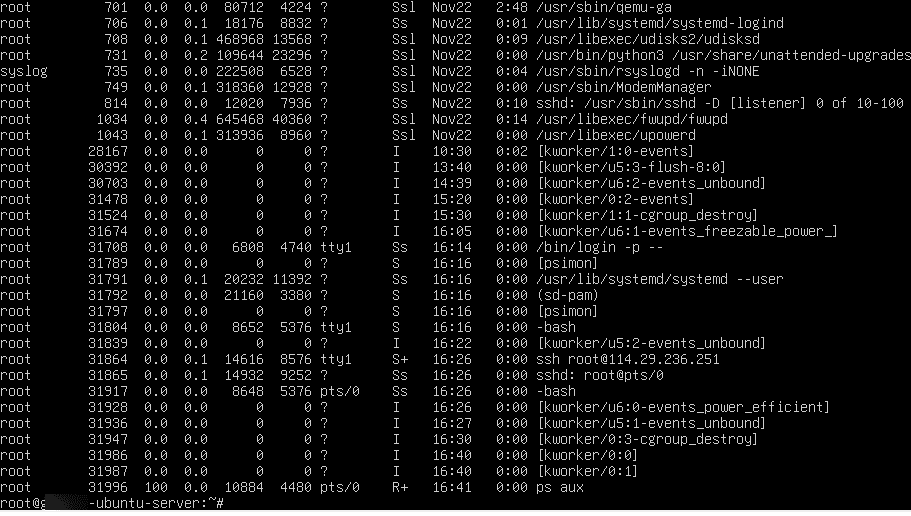
- To see all running processes:
Command:
ps aux
5. Memory usage:
- To show memory usage
Command:
free –h
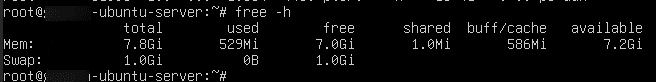
6. Manage Files and Folders:
- To list files in current directory
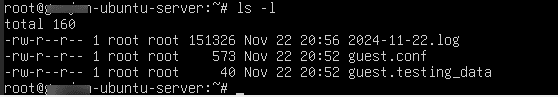
Command:
ls –l
- Create a text file
Command:
touch /path/to/directory/myfile.txt
- Delete a file
Command:
rm /path/to/file/myfile.txt
- Create a folder
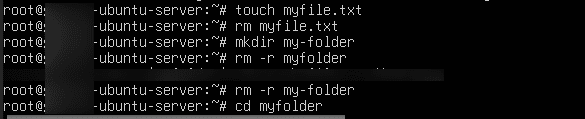
Command:
mkdir /path/to/directory/my-folder
- Delete a folder and its contents
Command:
rm -r /path/to/folder/my-folder
- Change directory
Command:
cd /path/to/directory
7. Update server
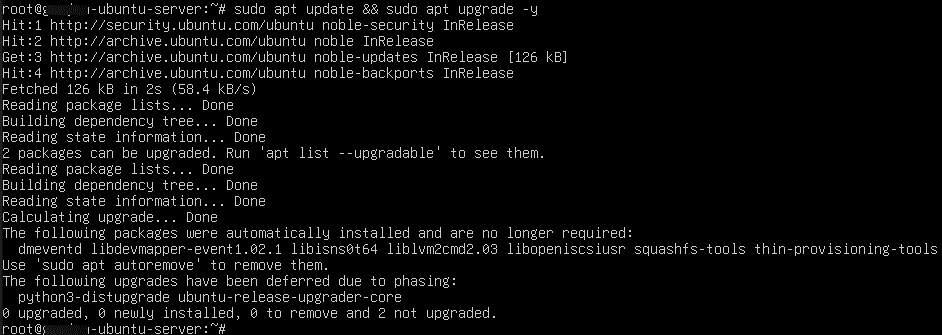
- Update package lists and update packages
Command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade –y
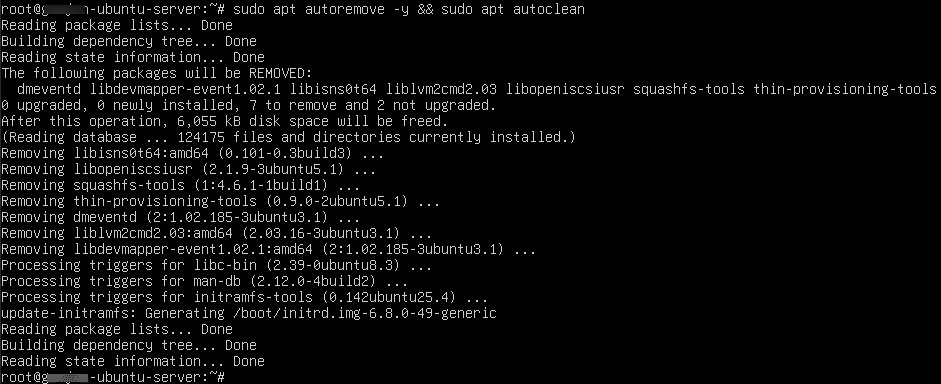
- Clean up necessary packages and files
Command:
sudo apt autoremove -y && sudo apt autoclean
Install software
- Install software using apt
Command:
sudo apt install <software-name>
Note: For demo purposes, in place of software-name, Flameshot is entered (which is an open-source tool to take screenshots).
- Secure your server
Change SSH port
- Open SSH configuration file
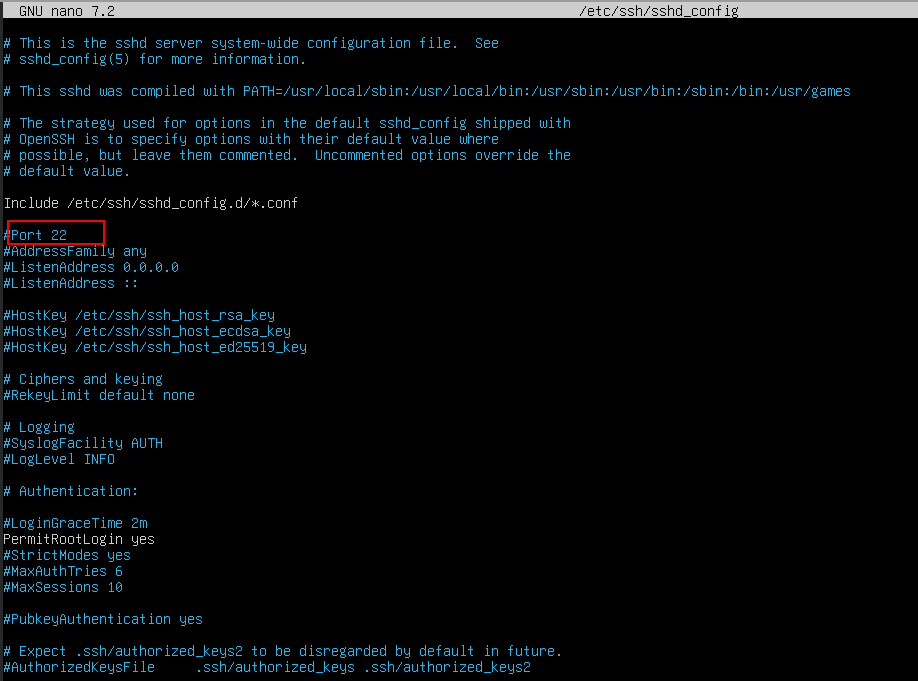
Command:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
![]()
Find line Port 22.
Modify the line to Port 2222.
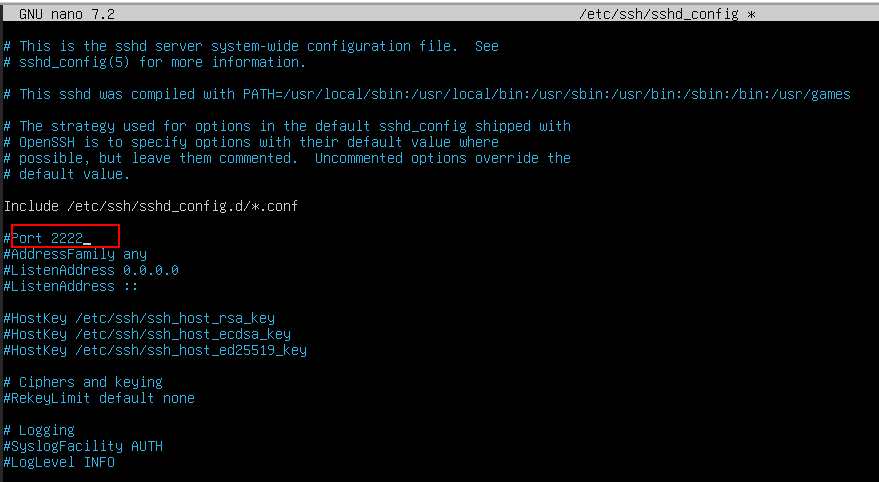
- Save and exit the file (press Ctrl+o to save the file, and Ctrl+X to exit the file).
- Now, restart SSH service by running the below command
Command:
sudo systemctl restart ssh
![]()
Setup Firewall
- First enable UFW
Command:
sudo ufw enable
- Allow new SSH port
Command:
sudo ufw allow 2222/tcp
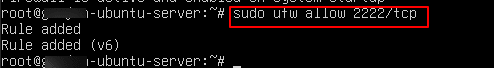
- Check UFW rules and status
Command:
sudo ufw status
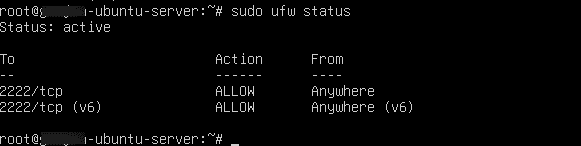
2. SSH for Windows:
- In the start menu, type Windows PowerShell and select Run as Administrator.
- After connecting, you can use these simple commands.
Check Server status
- To know the name of the currently logged-in user
Command:
whoami
- To see who has logged in
Command:
query user
- To check Disk space
Command:
Get-PSDrive
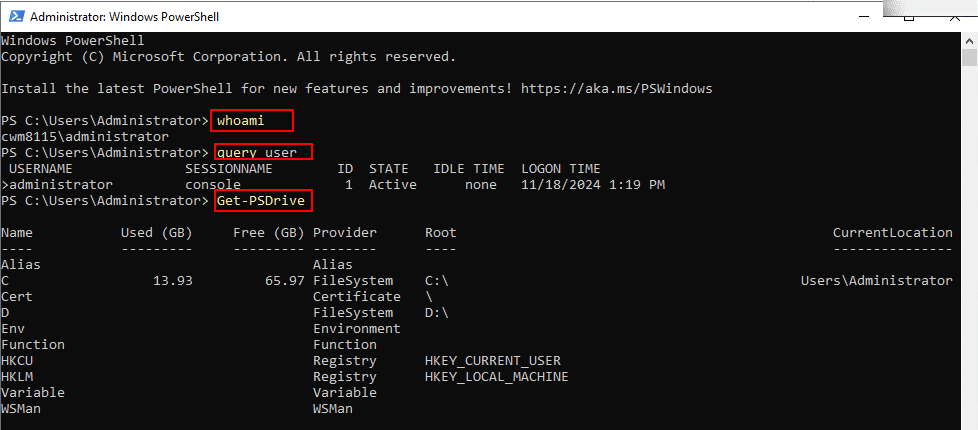
- To see running processes
Command:
Get-Process
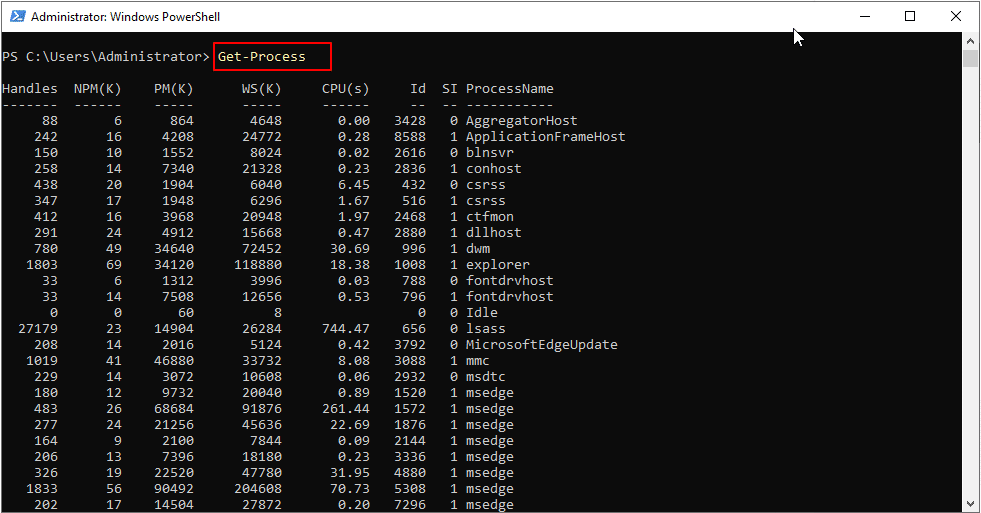
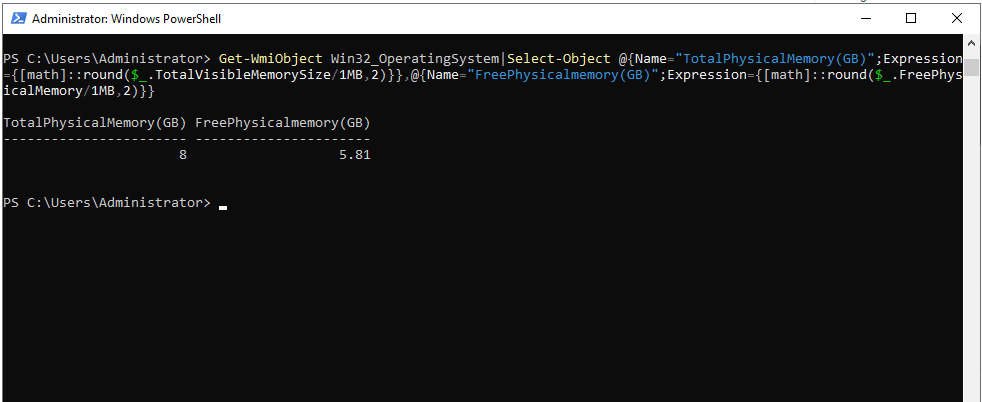
- To show memory usage
Command: >pre>
Get-WmiObject Win32_OperatingSystem | Select-Object @{Name="TotalPhysicalMemory(GB)";Expression={[math]::round($_.TotalVisibleMemorySize/1MB,2)}}, @{Name="FreePhysicalMemory(GB)";Expression={[math]::round($_.FreePhysicalMemory/1MB,2)}}
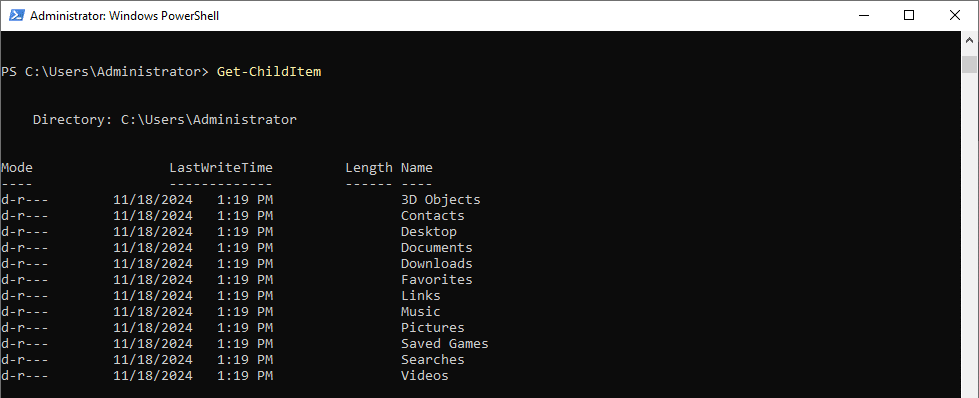
3. Manage Files and Folders:
- To list files
Command:
Get-ChildItem
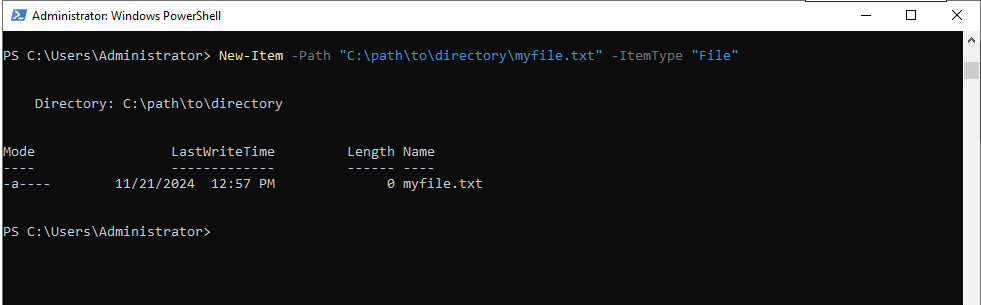
- To create a text file
Command:
New-Item -Path "C:\path\to\directory\myfile.txt" -ItemType "File"
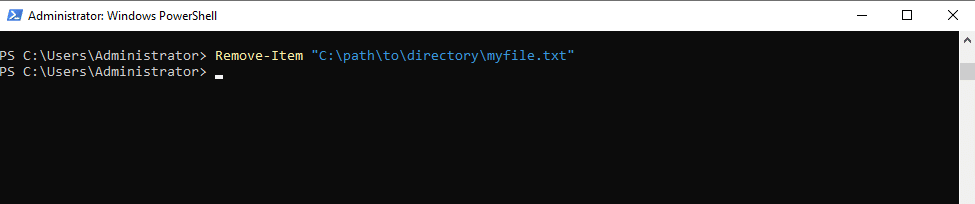
- To delete a file
Command:
Remove-Item "C:\path\to\file\my-file.txt"
- To create a folder
Command:
New-Item -Path "C:\path\to\directory" -Name "my-folder" -ItemType "Directory"

- To delete a folder and its contents
Command:
Remove-Item "C:\path\to\folder\my-folder" -Recurse
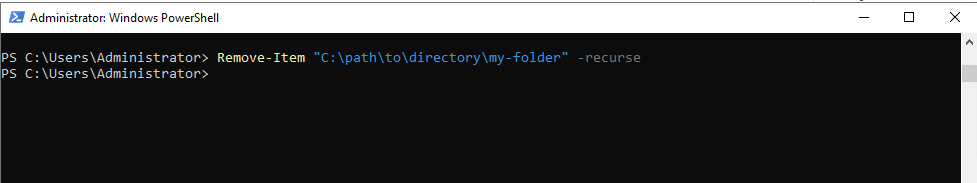
- To change directory
Command:
Set-Location "C:\path\to\directory"
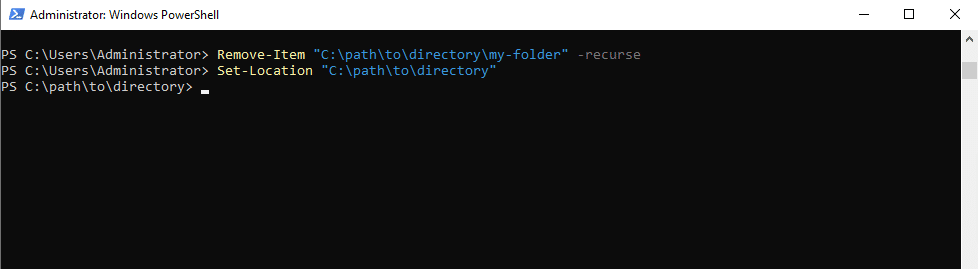
4. Update Server:
- The below commands require PSWindowsUpdate module. So, first install this module by running the below command.
Command:
Install-Module -Name PSWindowsUpdate -Force -Scope CurrentUser
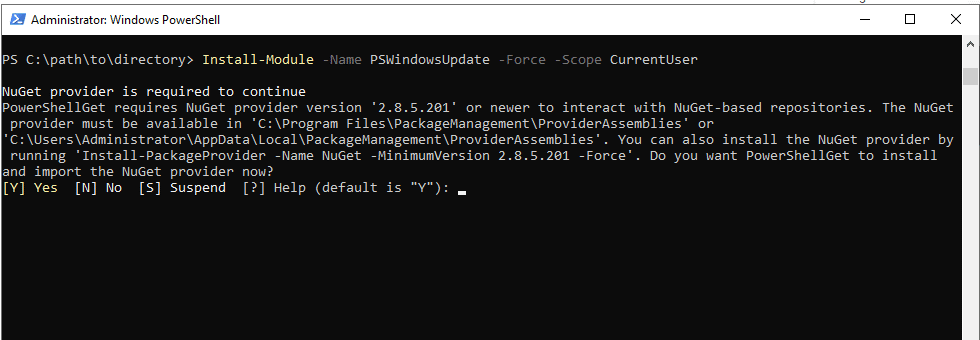
- Check for updates
Command:
Get-WindowsUpdate

- Install updates
Command:
Install-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll –AutoReboot
5. Install software
- To install software on Windows using PowerShell, you can use Chocolatey (a package manager for Windows). First, you need to install it by running the below command:
Command:
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force; [System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [System.Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12; iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://community.chocolatey.org/install.ps1'))
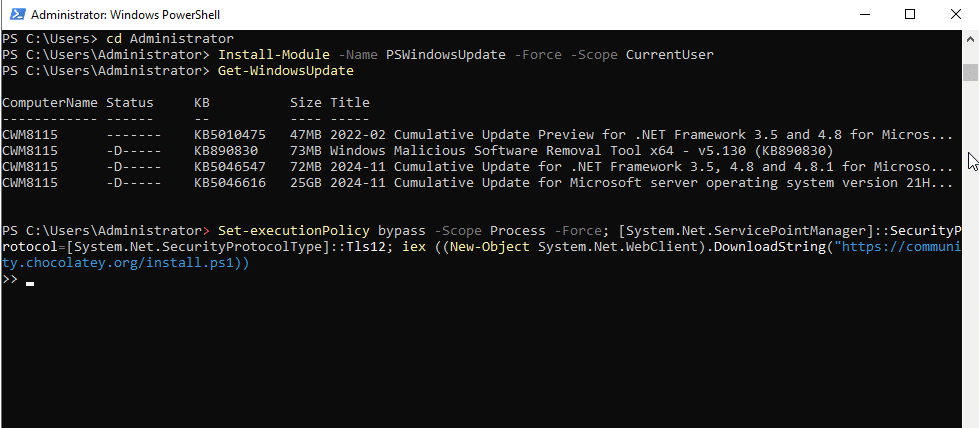
- Once installed, you can install software by running the below command
Command:
choco install <software-name>
6. Secure your Server
- Open PowerShell in the start menu and select Run as Administrator.
- To check OpenSSH Server feature is available or not, run the below command.
Command:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | Where-Object Name -like 'OpenSSH*'
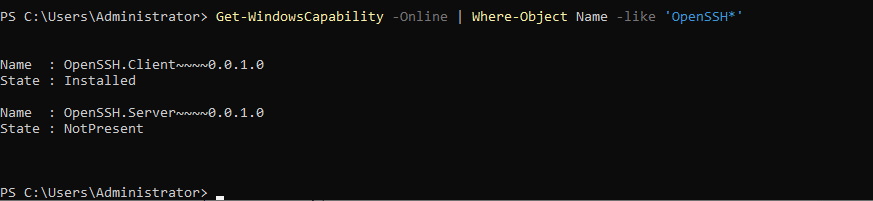
- If it says OpenSSH Server is not present, the install OpenSSH Server. Then install it by running the command below.
Command:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0
- Verify the installation by running the below command.
Command:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | Where-Object Name -like 'OpenSSH*'
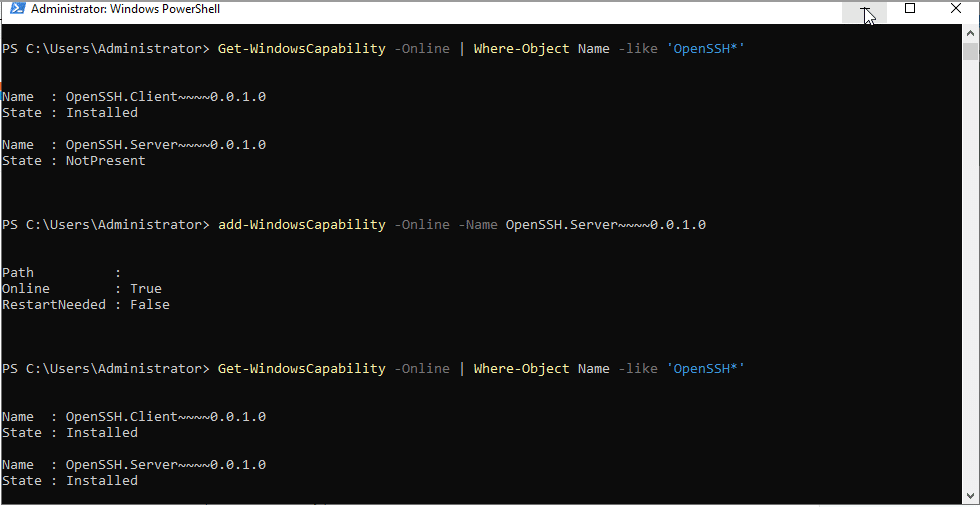
- Start the OpenSSH Service by running the below command.
Command:
Start-Service sshd
Set-Service -Name sshd -StartupType Automatic
To know the status of OpenSSH Service, run the below command.
Command:
Get-Service -Name sshd
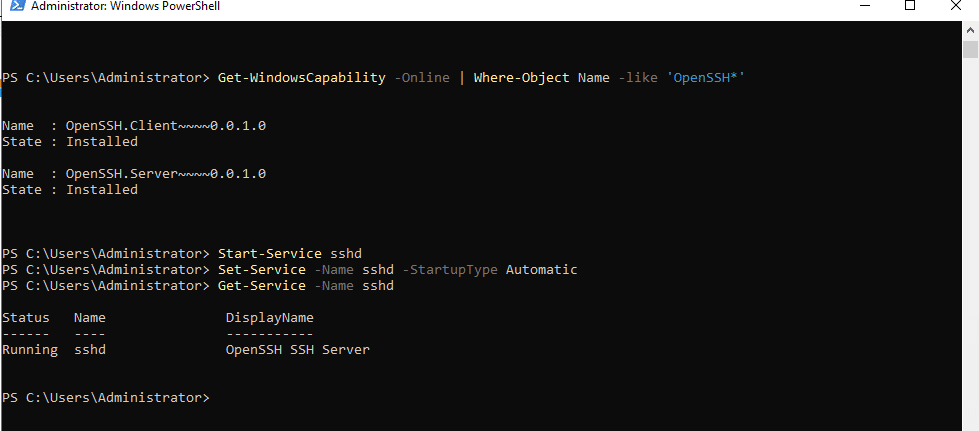
- Ensure that Port 22 is open on Windows Firewall.
Command:
New-NetFirewallRule -Name sshd -DisplayName "OpenSSH Server (SSH)" -Enabled True -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 22 -Action Allow
- Test the SSH port by running the below command
Command:
ssh localhost
If successful, you will see a login prompt. Enter your credentials, then you will see a new screen.
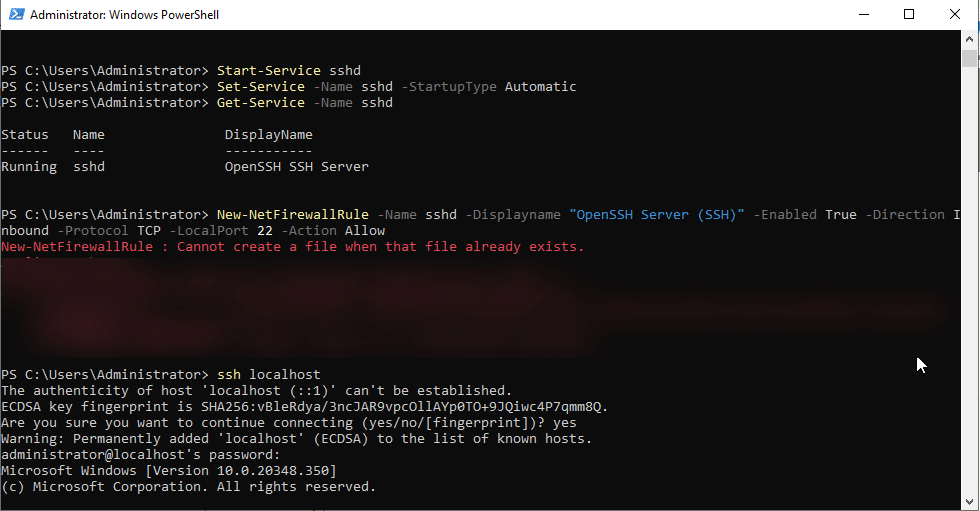
Now, you are in shell.

7. Setting up a firewall
Windows does not use SSH by default for remote administration. However, if you’re using OpenSSH Server on Windows, you can change the SSH port by modifying the SSH Server configuration file and update your firewall settings.
- Locate the sshd_config file by running the below command.
Command:
C:\ProgramData\ssh\sshd_config
- Select Notepad and click OK.
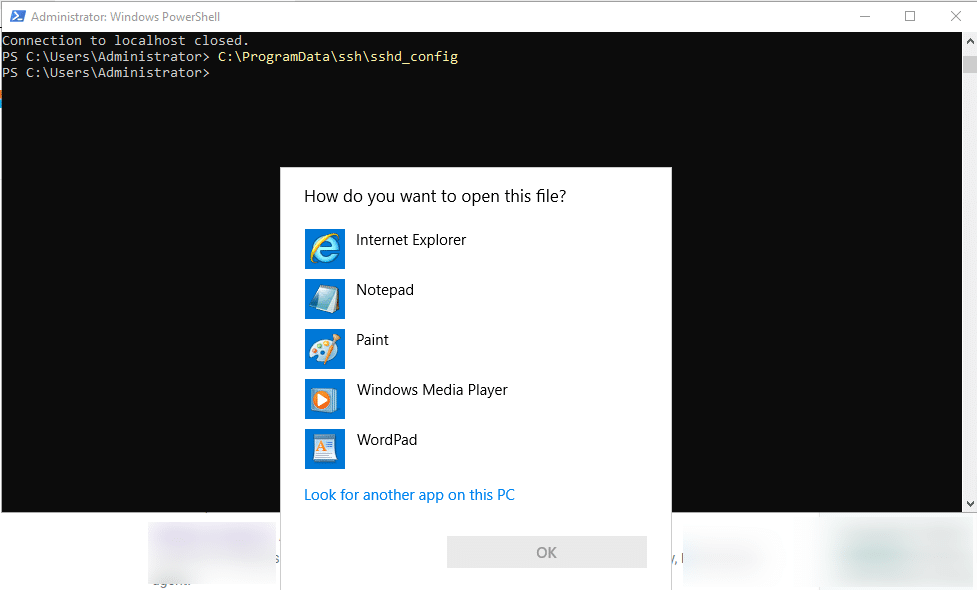
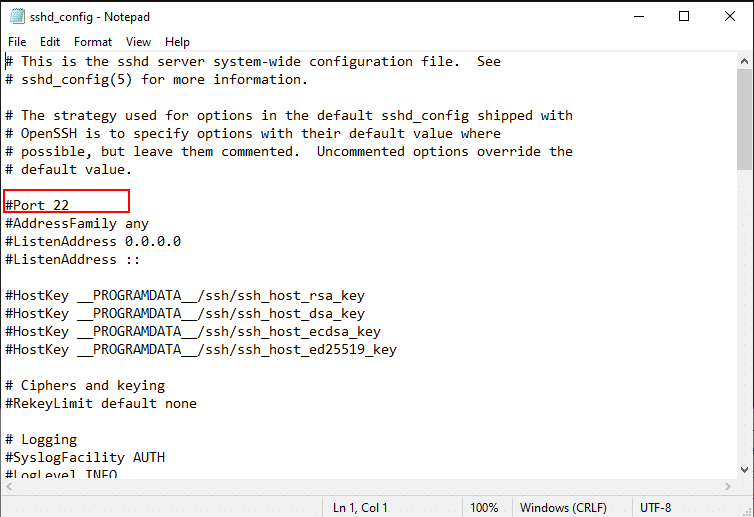
Find #Port 22.
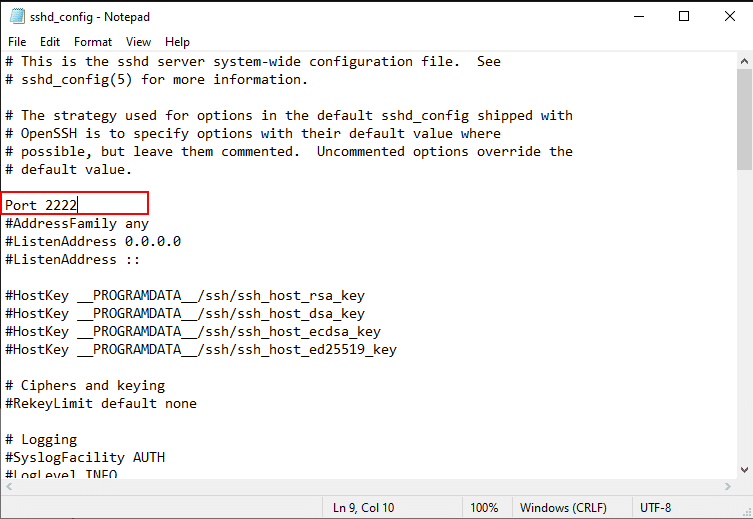
Now, uncomment the line and change the port to 2222. Save and close the file.
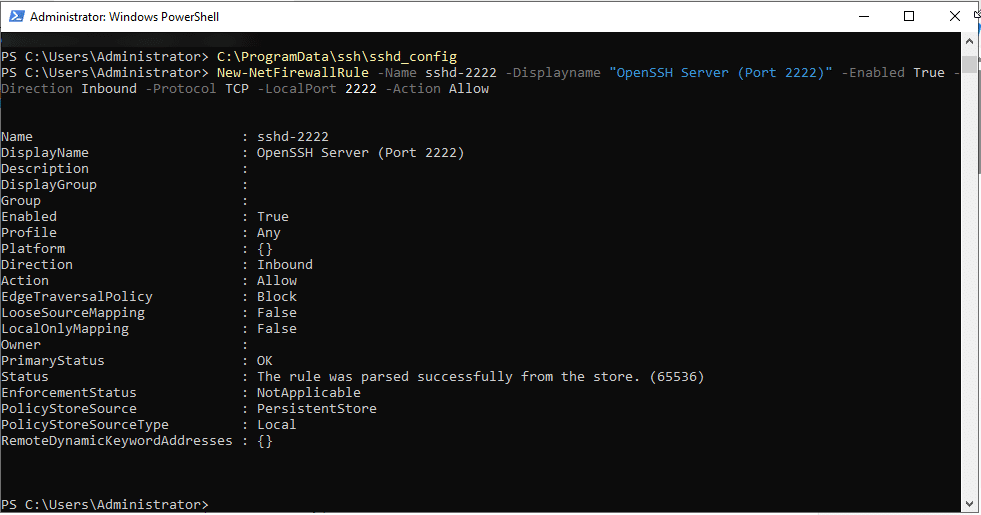
- After changing the port, you need to update the Windows firewall to allow traffic on new port.
Command:
New-NetFirewallRule -Name sshd-2222 -DisplayName "OpenSSH Server (Port 2222)" -Enabled True -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 2222 -Action Allow
- Restart the SSH by running the below command.
Command:
Restart-Service sshd
Verify the service is running or not.
Command:
Get-Service sshd
You will see the server is running.
Connect to your SSH server using new port.
Command:
ssh username@localhost -p 2222 (Replace username with your Windows Username).
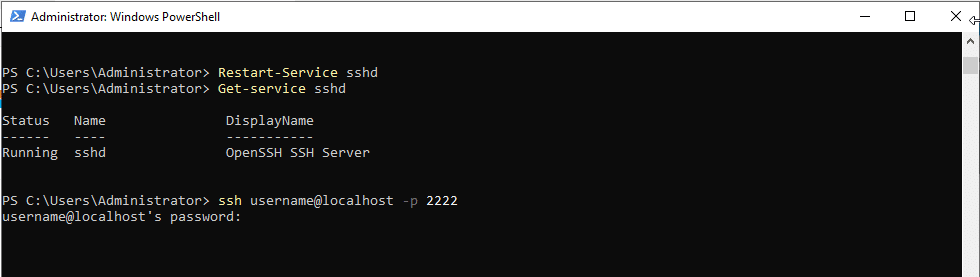
- Verify the server is listening on new port.
Command:
netstat -an | findstr 2222
You will see the message as shown in the screen below.

And that’s it! You have now learned how to use command line tools on a Kamatera server.