Cloud Computing Advantages and Disadvantages
Cloud

Everyone seems to be migrating something to the cloud these days. With a market already topping $540 billion and 9 out of 10 companies using cloud services in some form, cloud computing has become a business necessity.
While the cloud industry is expected to continue its breakneck growth, not everyone’s getting the results they expected. Many businesses jump into a cloud-based solution, only to find themselves facing unexpected challenges, spiraling costs, or performance issues they never anticipated.
The many benefits of cloud computing include enhanced collaboration across time zones, automatic updates, and improved recovery solutions. But it also presents challenges like cloud security concerns, business continuity issues, and potential downtime. Whether you’re still weighing your first cloud migration or questioning if your current setup is delivering what was promised, we’ll help you understand the advantages and disadvantages of cloud computing.
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing enables widespread, customizable access to a remote network of combined computing resources like networks, servers, storage, applications, and services. Users can quickly and easily enable services with minimal effort or interaction with a cloud service provider.
The cloud model’s benefits for the companies include: automatic access to computing on demand, broad access network, resource pooling, multi-tenant model, rapid elasticity (fast and flexible access to resources), and measured service (automatic control and resource optimization that uses a pay-per-use model).
There are 5 main types of cloud computing (private, public, multi-cloud, cloud for the community, and hybrid cloud) and three service models: infrastructure-as-a-service (access to remote physical or virtual machine model service), platform-as-a-service (typically including the operating system, which includes data storage, and web servers to develop software applications), and software-as-a-service (access to cloud storage and software applications).
How cloud infrastructure really works
Cloud infrastructure is a sophisticated ecosystem of physical and virtual components that work together seamlessly. It typically refers to the hardware, virtual resources, cloud storage systems, and networking components, and is delivered through infrastructure as a service (IaaS) models by providers such as Kamatera. The cloud servers and their accompanying networking hardware, cloud storage, and virtualization software live in data centers spread across various worldwide locations for redundancy and low latency.
Cloud management involves the administration, monitoring, and optimization of cloud resources. This includes deploying virtual machines, configuring storage, managing data traffic, and ensuring security.
Management tools and platforms are used to automate scaling, monitor resource usage, and maintain performance standards. Your cloud computing provider can also help you with cost optimization, ensuring that you only pay for the resources you consume.
Key aspects of cloud infrastructure management include:
- Resource allocation: cloud computing tools dynamically distribute computing power, data storage, and bandwidth based on demand.
- Security and compliance: protecting data and ensuring adherence to data residency regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Performance monitoring: tracking system health and optimizing performance.
- Backups and recovery: implementing strategies for data redundancy and quick disaster recovery from outages.
Advantages of cloud computing
Cloud computing services can truly transform how your business operates—they grow when you need them to, bounce back from problems faster, and often cost less than maintaining your own servers. But it doesn’t happen automatically. Cloud infrastructure and management require careful planning and management to ensure that your cloud platform is secure, reliable, and scalable.
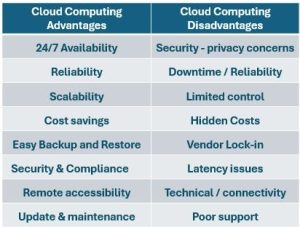
These are some of the key advantages of cloud computing:
Cost efficiency: Cloud computing eliminates the need for substantial upfront investments in hardware and software. Organizations only pay for the resources they use, reducing capital expenditure and improving cost savings.
Scalability and flexibility: Cloud services can be easily scaled up or down based on demand. This flexibility allows businesses to adjust their computing power instantly, supporting growth and fluctuating workloads without disruptions.
Disaster recovery and data backup: Cloud providers typically offer robust backup and disaster recovery solutions, ensuring data protection and minimizing downtime during unforeseen events.
Remote accessibility: You can access data and cloud-based applications and data from anywhere with a consistent internet connection, enhancing collaboration and enabling remote work.
Security and compliance: Leading cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, including encryption and multi-factor authentication, to protect data. Many also comply with global standards like GDPR and HIPAA.
Automatic updates and maintenance: Cloud providers handle software updates and maintenance, allowing organizations to focus on core business activities instead of IT management.
Overall, cloud computing enhances operational efficiency, reduces costs, and supports business agility, making it a cornerstone of modern IT strategy.
Disadvantages of cloud computing
While cloud computing offers numerous advantages, it’s crucial to acknowledge its potential drawbacks. Before making a full transition, businesses should carefully evaluate these challenges to ensure that cloud adoption aligns with their specific requirements and risk tolerance. Some of the disadvantages of cloud computing include:
Cloud computing security and privacy concerns are major issues, as sensitive data is stored off-premises, making it vulnerable to cyberattacks and unauthorized access. Cloud providers implement security measures, but data breaches and security risks remain a concern, especially for industries with strict regulations.
Downtime and reliability are also problematic. Cloud services depend on internet access, so outages or slow internet can disrupt connectivity. Even major cloud providers occasionally experience internet connection outages.
Limited control over infrastructure and backend processes is a challenge for organizations with specific customization needs. Cloud storage providers might not provide the right data storage setup, which can restrict direct access and control.
Finally, hidden costs can emerge from data retrieval fees, unexpected scaling, or potential security threats, making budgeting unpredictable.
Overall, while cloud computing drives innovation and efficiency, it requires careful planning to manage risks related to security, reliability, cost, and control.
Future outlook
The future of cloud computing is poised for exciting advancements. We can expect to see increased integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) capabilities, enabling more sophisticated automation and predictive analytics. Serverless architecture will likely become even more prevalent, allowing developers to focus solely on writing code without managing underlying infrastructure. Edge computing will also play a significant role, bringing cloud capabilities closer to data sources, which will reduce latency and improve performance, particularly for IoT and real-time applications.
The evolution of cloud computing will also probably involve a greater emphasis on sustainability and security. Cloud providers will face increasing pressure to adopt eco-friendly practices and offer enhanced security measures to protect valuable data. The development of more robust and standardized multi-cloud and hybrid-cloud solutions will also be crucial.
Is cloud computing right for you?
For most companies, the answer is yes, the advantages outweigh the disadvantages of cloud computing. Today is the best moment to start rebuilding or re-architecting your apps to be cloud-native and fully utilize the cloud. An application modernization evaluation and an initial pilot project to test the limits of cloud technology might be the first steps in your journey.


