Why Your Business Needs a Smart Cloud Migration Strategy
Cloud
If your organization has outgrown its legacy, on-prem systems, then it might be time to migrate to the cloud. A well-defined cloud migration strategy is crucial for businesses to modernize their IT infrastructure in the best and most cost-efficient manner. The cloud is where your competitors are, where your customers are, and you should be there, too.
Why Do You Need a Cloud Migration Strategy?
If you’re still wondering whether to spend your time crafting a cloud migration strategy, let us explain why you should. Having a well-thought-out strategy will help you answer crucial questions, such as: Which of your applications are ready for the big move to the cloud? Which is right for your data: public, private, or hybrid cloud solution? And perhaps most importantly, how will you ensure your sensitive customer data continues to be secure and compliant during the move?
Here is a list of some of the key advantages to having a cloud migration strategy:
Business Agility
Having your apps on the cloud will enable you to react swiftly to market shifts and demands. If you can be flexible enough to adjust resources as needed, you’ll be better positioned to seize opportunities at the best rate.
Improved Collaboration
Cloud environments let your teams collaborate more effectively by giving you ubiquitous access to common tools and data. This results in better productivity and efficient workflows.
Cost Efficiency
Cloud migration will reduce your costs and expenses related to hardware and infrastructure. Also, you can choose the pay-as-you-go pricing model of cloud services, which ensures you only pay for what you use.
Disaster Recovery/Business Continuity
To minimize downtime and data loss, cloud providers should offer sophisticated disaster recovery solutions to guarantee that data is regularly backed up and can be restored quickly.
Enhanced Security
Cloud providers offer improved protection that would be difficult to achieve by yourself. Also, you’ll be compliant with industry regulations for your cloud services.
Focus on Core Business
By moving IT management to cloud providers, you can focus your efforts on main business processes. This will allow you greater innovation and the ability to explore new business opportunities.
Options of Cloud Migration Strategies
Although there’s no one-size-fits-all approach, here are a few different strategies that you can review, each suited to different needs and scenarios. They range from a quick and simple move to completely writing and recreating applications. Each option has its pros and cons. Read on to see which could be right for your organization.
Rehosting (Lift and Shift)
One method to perform cloud migration is rehosting (lift and shift). Rehosting means moving your current application and data to cloud infrastructure with minimal or no redesign or modification. This usually means moving to a cloud services provider.
The main benefits of rehosting migration are simplicity and cost-effectiveness. You can set it up quickly with low, if any, downtime. You can choose this approach if you don’t have many engineers with the skills to perform in a cloud migration. Rehosting your current application does not require deep cloud knowledge.
A possible drawback is that technical difficulties can always happen. There will always be a risk that the migration will fail or ongoing problems will crop up, which could affect your business.
Replatforming (Lift, Tinker, and Shift)
Re-platforming method lies between rehosting and a refactor migration, so it’s called the lift-tinker-and-shift approach. You don’t modify the code as much as when you refactor, but some changes must be implemented to adapt to the new cloud infrastructure.
Re-platforming gives you access to new features and prepares you for future growth. If you know you aren’t prepared to scale fully, you can consider this intermediate variant. It puts you on the cloud, but in case things don’t go according to plan or there are delays, it doesn’t put all your eggs in one basket.
Refactoring/Re-architecting
Refactoring migration means changing existing applications so they can work on the cloud. It is quite different from rehosting. In refactoring, you create new applications (code) that will work with your new cloud-based server.
Refactoring guarantees that the migration is done accurately. It’s the best choice if you can take a little risk. The biggest disadvantage is the high price you’ll pay. The most costly and time-consuming approach for cloud migrations is refactoring. But if you choose a different migration route, you may encounter migration issues and losses. In the long run, refactoring could save you money.
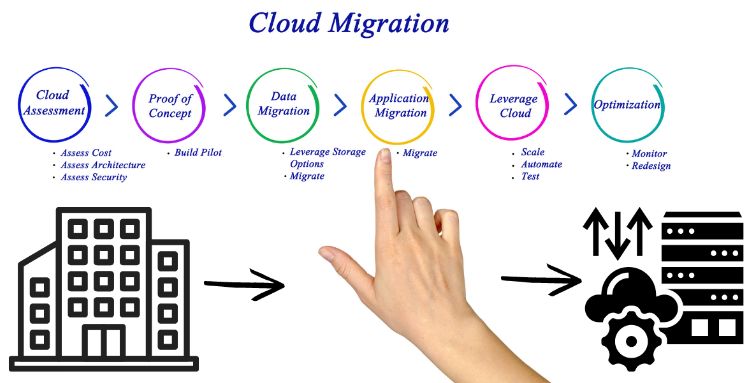
Rebuild (Cloud-Native Development)
By using the rebuild migration approach, you’ll recreate the entire application as a PaaS infrastructure. It’s different from refactoring, where you only change parts of the application.
When you rebuild, you delete the old code and rewrite the application in the cloud so you can take advantage of all the new cloud platform’s capabilities. A cloud-native application is very scalable and inexpensive to use. But beware, rebuilding your application from scratch has its cost.
Replace
With the replace migration strategy, you utilize SaaS to fully replace your existing application. If your current SaaS applications can offer all the features you need, migrating them to the cloud will reduce your IT development expenses.
Migration Processes and Methods
To go all at once or in waves? To be flexible or have a strict structure? When embarking on a cloud migration journey, organizations can take guidance from several processes and methods, each suited to different requirements and complexities. Let’s look at a few options.
Agile migration approach
By utilizing the agile approach, you will deliver value to clients more quickly and effectively because of the changing requirements and feedback. Some cloud migration processes can benefit from approaches that include collaborative development, more flexibility and visibility, and continual improvement.
Here are some steps to incorporate agile methodology in your cloud migration project:
- Identify the project goals: Determine the objectives of the cloud migration project and ensure that all team members agree with them.
- Break down the work: Apply techniques like user stories and epics to break the job down into smaller, more manageable chunks that may be finished in brief iterations.
- Prioritize: Ensure all team members understand the priorities, by scheduling the work based on business value, risk, and technical complexity.
- Collaborate with stakeholders: To facilitate communication and collaboration, use tools like daily stand-up meetings, sprint reviews, and retrospectives.
- Monitor the progress: Adjust your process and utilize tools such as burndown charts to stay on track and meet your goals.
Wave Planning and Batching
If your migration is truly large-scale, you’ll need wave planning. You can group similar applications in a wave plan by considering infrastructure, application design, business functionality, and application requirements (e.g. a shared database). Then, you discuss the wave plan with the infrastructure and application teams to ensure they will be available at the determined migration time.
Some of the best practices for wave planning include:
- Plan 4 or 5 waves ahead of time. This will guarantee that the migration teams will always have adequate servers.
- Fail fast. You should start with a few, simple applications and apply your learnings to later waves.
- Steadily introduce more complexity and servers into the waves as you progress.
- During the early waves (1–4), migrate fewer servers (< 10), non-complex applications, and applications in low environments, e.g. development or test servers.
- Wave planning is not a one-time task; it’s an ongoing process. Don’t plan all your waves at once.
Testing and Validation Processes
To test and validate your cloud environment, you might need to use various testing tools and techniques, depending on the scope and goals of your testing. For instance, load testing can assist you in assessing your cloud environment’s performance, dependability, and scalability under pressure.
To ensure that the cloud environment fulfills your expectations and brings you value, you can apply functional testing to your servers, apps, and websites. Security testing includes the security assessment and compliance of your cloud environment against multiple threats and vulnerabilities. By integration testing, you test the interoperability of your cloud environment with other systems (applications).
You should perform testing and validate the functionality of your cloud infrastructure by comparing baseline and target metrics. Baseline metrics show your on-premises or legacy systems before migration, while target metrics are values of your cloud infrastructure after migration. By comparing the two, you can measure the effect of your cloud migration and assess whether you have accomplished the expectations.
Conclusion
For small and medium-sized businesses, moving the cloud won’t be the solution to every problem, but it offers certain advantages. And if you don’t capitalize on its benefits, your company could lag behind others in your industry. Utilizing one of these cloud migration strategies will help you smoothly transition to the cloud and ensure that the infrastructure and products you invest in are efficient and cost-effective.


